Managing diabetes is about more than just medication—it’s about making daily choices that protect your health. One of the most important goals is to keep blood sugar levels under control with diabetes. This means balancing your diet, physical activity, and lifestyle habits to prevent dangerous spikes and drops in glucose levels. With a few practical steps, you can live well and reduce the risk of complications.
Why blood sugar control matters
Blood sugar control is the foundation of diabetes management. High blood sugar over time can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to problems like heart disease, kidney issues, and vision loss. In contrast, low blood sugar may lead to dizziness, confusion, or even fainting.
By monitoring your glucose levels regularly and making smart lifestyle adjustments, you can stay within a healthy range most of the time. Consider it a daily investment in your future health.
Healthy eating habits to keep blood sugar levels under control with diabetes
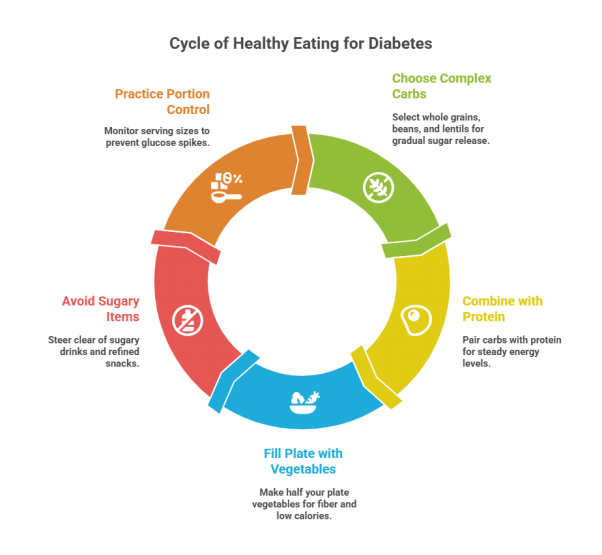
Food choices have a direct impact on your glucose readings. The aim is to eat balanced meals that provide steady energy without sudden spikes.
- Opt for complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, beans, and lentils, as they release sugar gradually.
- Combine carbohydrates with protein to keep energy levels steady—for instance, whole grain toast with eggs.
- Make half your plate vegetables, since they are high in fiber and low in calories.
- .Avoid sugary drinks and refined snacks, which can quickly raise blood sugar.
- Portion control is also key. Even healthy foods can raise glucose if eaten in large amounts, so keep an eye on serving sizes.
The role of regular physical activity
Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, lowering glucose levels naturally. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Strength training twice a week also benefits blood sugar control by building muscle, which uses more glucose for energy. Be sure to monitor your blood sugar before and after exercise to prevent it from dropping too low
Monitoring and adjusting your routine
Keeping track of your blood sugar readings helps you see how food, activity, stress, and sleep affect your glucose. This allows you to make informed decisions.
If you notice patterns—such as high readings in the morning or after certain meals—discuss them with your healthcare provider. Adjustments to your meal plan, exercise schedule, or medication may be needed.
Managing stress and sleep
Stress triggers the release of hormones that raise blood sugar, while poor sleep affects insulin sensitivity. To manage stress, try deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga.
Aim for 7–8 hours of sleep each night. Good sleep hygiene—like going to bed at the same time and limiting screen use before bed—can make a big difference in glucose stability.
Small lifestyle tweaks that make a big impact
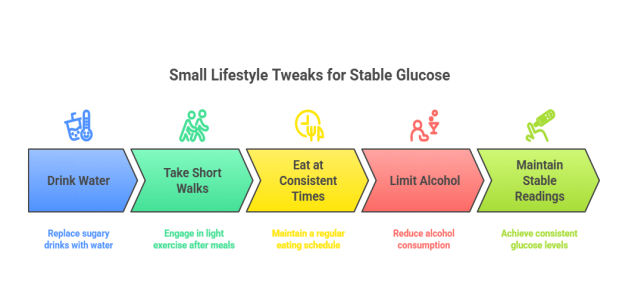
Sometimes, it’s the little changes that add up:
- Drink water instead of soda or juice.
- Take short walks after meals to help your body use glucose.
- Eat at consistent times to avoid sudden drops or spikes.
- Limit alcohol, as it can cause unpredictable glucose changes
By making these small shifts, you’ll find it easier to maintain stable readings
Living well with diabetes through consistent habits
Learning to keep blood sugar levels under control with diabetes is not about perfection—it’s about consistency. The more you make healthy eating, regular movement, and mindful living part of your routine, the better you’ll feel and the lower your risk of complications.
Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, yet with the right approach, you can live an active, rewarding life. Your daily habits have the power to shape your health future—starting today.
At Erode Diabetes Foundation (EDF), in collaboration with MMCH, we are committed to helping individuals take control of their health and live well with diabetes. Learning to keep blood sugar levels under control with diabetes is not about perfection—it’s about building consistency in your daily routine. By making healthy eating, regular physical activity, and mindful living a part of your lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications.


