Obesity impacts millions of people worldwide. Beyond visible weight gain, it can trigger a range of internal issues, including chronic inflammation. Understanding Obesity and chronic inflammation is essential because it highlights hidden risks that often go unnoticed. This relationship is often overlooked, yet it can trigger significant health risks if neglected.
What is chronic inflammation?
· Acute inflammation is the body’s natural defense. For example, when you get a cut or infection, inflammation helps your body heal.
· Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is when the immune system stays active for too long. Instead of helping, it slowly starts damaging healthy tissues.
· In people with obesity, excess fat cells release chemicals that keep the immune system in a constant “alert mode.”
· This ongoing inflammation can affect important parts of the body such as the heart, joints, and vital organs.
· Over time, chronic inflammation increases the risk of serious health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
How obesity triggers inflammation
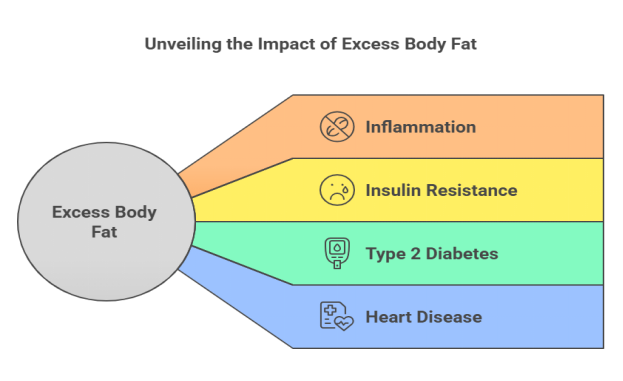
Excess body fat is not just a storage of energy, it is active tissue that produces chemicals called adipokines. These chemicals can promote inflammation throughout the body. Studies show that individuals with obesity often have elevated levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP). This ongoing immune response contributes to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
The role of lifestyle in managing inflammation
Diet and exercise are key factors in managing long-term inflammation A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grain foods, and good heart friendly fats may reduce inflammation in the body. Similarly, regular exercise helps lower body fat and improve immune function. Stress management and sufficient sleep are also vital, as stress hormones can worsen inflammation.
Health risks linked to Obesity and chronic inflammation
The hidden connection between obesity and chronic inflammation increases the risk of several serious conditions. Heart disease, diabetes, liver problems, and even some cancers have been linked to chronic inflammation in individuals with obesity. Recognizing these risks early allows for lifestyle adjustments and medical intervention, helping prevent long-term damage.
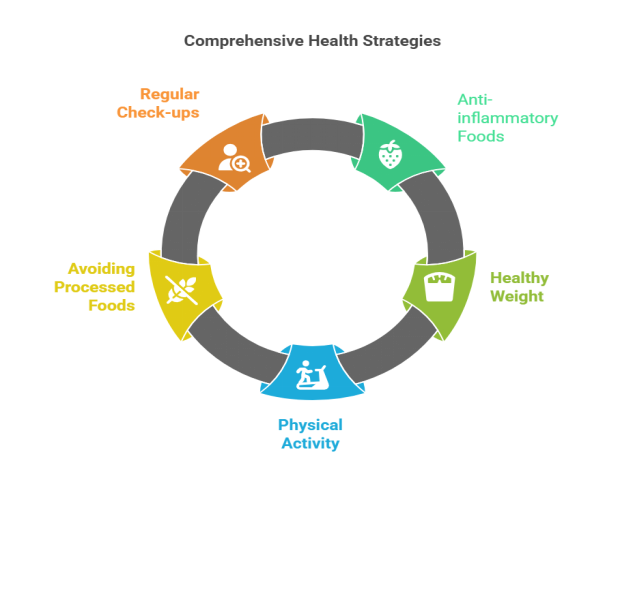
Strategies to reduce inflammation and support health
· Eat more foods that fight inflammation like fish (omega-3), berries, green leafy veggies, and nuts.
· Keep your body weight in a healthy range.
· Stay active with regular exercise for 45 minutes or daily movement of atleast 7000 steps.
· Cut down on junk food, sugary snacks, and too much alcohol.
· Go for regular health check-ups to catch any problems early.
Stay ahead of health risks
At Erode Diabetes Foundation (EDF), in collaboration with MMCH, we focus on raising awareness about the link between obesity and chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation can silently affect your body, even before obvious health issues appear. By identifying obesity early and making healthier lifestyle choices, such as eating nutritious foods, staying active, and monitoring key health indicators, individuals can lower their risk and improve overall well-being. Early awareness and consistent action are essential for preventing long-term complications and maintaining a healthier life.
we offer solutions to assess the obesity risks and make a plan accordingly to manage weight gain and prevent its complications.